Product
제품
-
Analytical Products
- Wyatt Technology
- Awareness Technology
- Eurofins l Abraxis (GSD)
- Aurora Biomed
- Canada NRC-CNRC
- Chrom Tech
- Eichrom Technologies
- EPROGEN
- Fluidic Analytics
- Globe Scientific
- GENERON
- Halo Labs
- Hygiena International
- KROMATON
- InProcess-LSP
- MTC Bio
- MZ-Analysentechnik
- Newomics Inc.
- Occhio Instruments
- Optimize Technologies
- Pickering Laboratories
- PolyLC
- Raykol Group
- RheoSense
- Rocker Scientific
- Santai Science
- SEDERE
- Spectra Analysis
- UCT
- Wealtec Corp
-
Bio & Medical Products
- Biolog
- Adooq Bioscience
- A&A Biotechnology
- Accegen Biotechnology
- Anatrace
- Array Bridge
- Biogenes GmbH
- BioQuochem
- BioServ UK
- Biomiga
- Biotech Support Group
- CinderBio
- Cell Technology
- Creative Biolabs
- Creative Diagnostics
- Creative Biostructure
- Creative Biomart
- Creative Enzymes
- EICOM
- Emulseo
- GLYcoDiag
- Helix Biotech
- InnoGenomics
- IsoSciences, LLC
- IUL Instruments
- Micropore Technologies
- Matrix Innovation
- PreciGenome
- PhylumTech
- ProFoldin
- Protein Ark
- Primer Design
- ProteoChem
- RareCyte
- RECIPE
- Silicycle Inc.
- Tymora Analytical
- UTAK
- YouSeq
- Z Biotech
- Fluoro ADP
- 제품명: Fluoro ADP
- 용도: Fluorescent ADP Detection Kit - Detection of ADP in tissue extracts/cell samples
- 메이커: Cell Technology
- 카달로그:
소개
Fluoro ADP
Fluorescent ADP Detection Kit - Detection of ADP in tissue extracts/cell samples
Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) is an organic molecule which plays a centralrole in cellular metabolism and energy transfer reactions. ADP is a product of ATP de-phosphorylation and can be rephosphorylated to ATP or further de-phosphorylation to AMP. This cycling of ADP is central to transferring potential (thermodynamic) energy from one source to another. Besides its involvement in glycolysis, citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation, ADP is also stored as dense bodies in blood platelets. Upon platelet activation, ADP is release which leads to further platelet activation through APD receptors (1-8).
Cell Technology’s Fluoro ADP assay provides a reliable, sensitive fluorimetric assay for the quantification of ADP inbiological samples.
1. Key Benefits
• Detection of ADP in cells or tissue extracts
• Detection of ADP in cell death, energy metabolism, mitochondria function
• ADP measurement in ATP consuming enzymes such as Kinases and ATPases
• ADP detection in Bacterial, Fungal and Plant Cells
• Fluorescent 96 well Plate Reader Readout (excitation: 530-570nm and emission at 590-600nm).
2. Assay Principle
The Fluoro ADP detection kit utilizes a non-fluorescent detection reagent, which is reduced in the presence ADP and a coupled enzyme reaction to produce its fluorescent analog. There is a linear relationship of ADP concentration to the fluorescent analog concentration. An ADP standard curve is generated to interpolate sample ADP concentrations. The kit can be used in both endpoint and kenitic modes.
Reaction:
1. ADP + Enzyme Coupled Reaction + Non-Fluorescent Detection Reagent→Fluorescent Analog + AMP
Detection: Excitation: 530-570nm and Emission at 590-600nm
2. 50µL of sample or ADP Standard + 50µL of Enzyme Reaction Cocktail -> Incubate 30 – 60 minutes; RT; DARK
Detection: Excitation: 530-570nm and Emission at 590-600nm
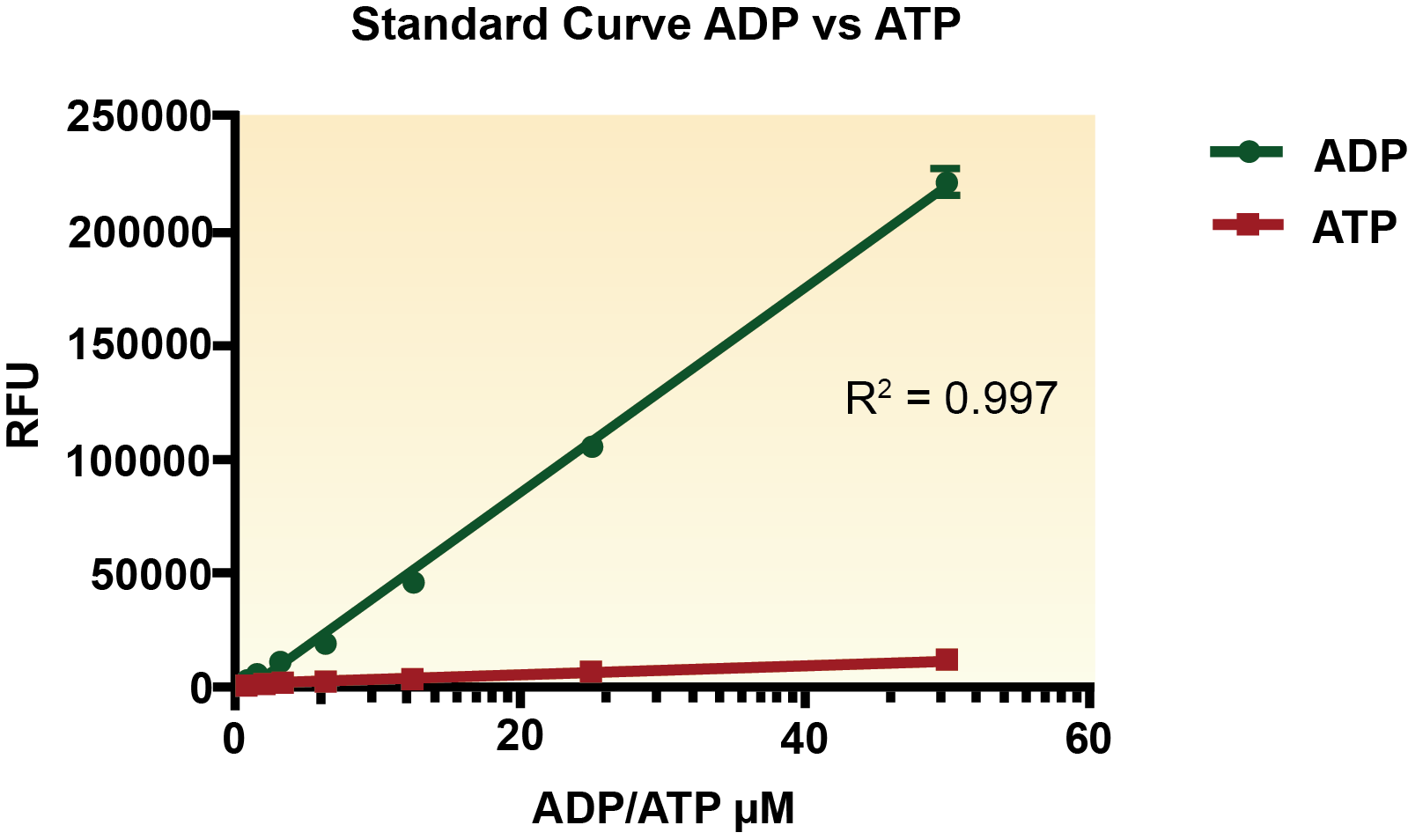
Figure 1. ADP vs ATP Standard Curve fitted with linear regression.
|
ADP mM Spike
|
% Recovery
|
|
50
|
93.08
|
|
12.5
|
92.04
|
|
1
|
118.48
|
Table 1. ADP was spiked into Jurkat cell samples. % Recovery was determined via linear regression from ADP standard curve. N=3 per sample.
주문정보
|
Reagent |
Part# |
Temperature |
|
Enzyme Mix 25X |
6031 |
-20°C |
|
Substrate Buffer |
3064 |
-20°C |
|
Detection Reagent 100X |
4028 |
-20°C |
|
ADP Standard 2.5 mM |
7025 |
-20°C |
|
NEM |
7026 |
-20°C |
관련자료
Reference
Cox, Michael; Nelson, David R.; Lehninger, Albert L (2008). Lehninger principles of biochemistry. San Francisco: W.H. Freeman. ISBN 0-7167-7108-X
Jensen TE, Richter EA (March 2012). "Regulation of glucose and glycogen metabolism during and after exercise". J. Physiol. 590 (Pt 5): 1069–76. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2011.224972. PMC 3381815PMID 22199166
Liapounova NA, Hampl V, Gordon PM, Sensen CW, Gedamu L, Dacks JB (December 2006). "Reconstructing the mosaic glycolytic pathway of the anaerobic eukaryote Monocercomonoides". Eukaryotic Cell. 5 (12): 2138–46. doi:10.1128/EC.00258-06. PMC 1694820 PMID 17071828
Medh, J.D. "Glycolysis" (PDF). CSUN.Edu. Retrieved 3 April 2013
Bailey, Regina. "10 Steps of Glycolysis"
"Citric Acid Cycle" (PDF). Takusagawa’s Note. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 March 2012. Retrieved 4 April 2013
"Biochemistry" (PDF). UCCS.edu. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-02-28
Murugappa S, Kunapuli SP (2006). "The role of ADP receptors in platelet function". Front. Biosci. 11: 1977–86. doi:10.2741/1939. PMID 16368572
